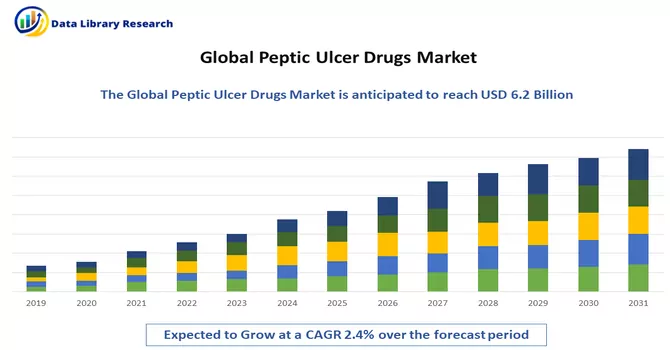
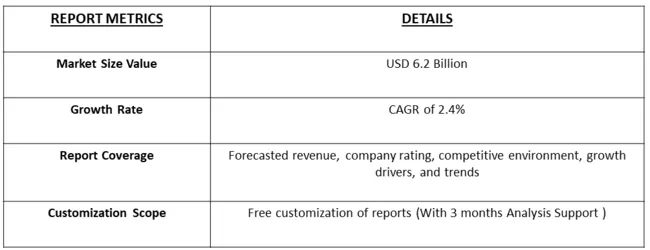
The global peptic ulcer drugs market size was valued at USD 6.2 in 2023 & is projected to reach a CAGR of 2.4% in forecast period, 2024-2031.
Get Complete Analysis Of The Report - Download Free Sample PDF
The peptic ulcer drugs market is characterized by a range of pharmaceutical interventions aimed at managing and treating peptic ulcers, including proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), histamine receptor antagonists (H2 blockers), antacids, and antibiotics. Peptic ulcers, which are open sores that develop on the inner lining of the stomach, small intestine, or esophagus, can cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, and nausea. Factors such as unhealthy lifestyle habits, stress, and infection with Helicobacter pylori bacteria contribute to the development of peptic ulcers.
The market for peptic ulcer drugs is driven by the high prevalence of peptic ulcers globally, especially in regions with high rates of H. pylori infection. Additionally, the rising geriatric population and the increasing incidence of risk factors such as smoking and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) use further contribute to market growth. Moreover, advancements in drug formulations, such as the development of combination therapies and sustained-release formulations, enhance treatment efficacy and patient compliance. However, challenges such as antibiotic resistance, side effects associated with long-term PPI use, and the availability of generic alternatives may restrain market growth. Overall, the peptic ulcer drugs market continues to evolve with ongoing research and development efforts aimed at addressing unmet medical needs and improving treatment outcomes for patients with peptic ulcers.
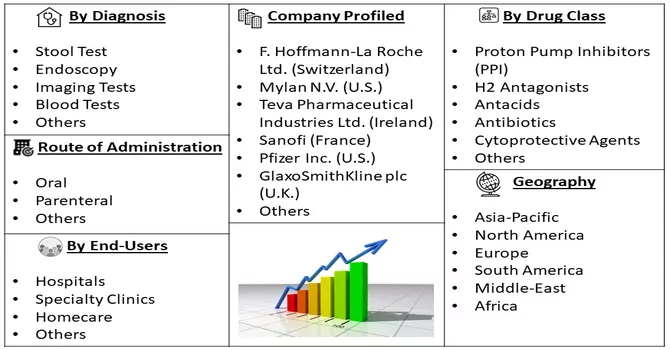
Market Segmentation: The Global Gastric Ulcers Market, By Diagnosis (Stool Test, Endoscopy, Imaging Tests, Blood Tests, Others), Drug Class (Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPI), H2 Antagonists, Antacids, Antibiotics, Cytoprotective Agents, Others), Route of Administration (Oral, Parenteral, Others), End-Users (Hospitals, Specialty Clinics, Homecare, Others) and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa, and South America). The report offers the value (in USD million) for the above segments.
For Detailed Market Segmentation - Download Free Sample PDF
Market trends in peptic ulcer drugs are shaped by several factors. One prominent trend is the increasing adoption of combination therapies, which involve the simultaneous use of multiple drugs to target different aspects of ulcer management, such as acid suppression, eradication of H. pylori infection, and mucosal protection. Combination therapies offer enhanced efficacy compared to monotherapy and are particularly beneficial in cases of severe or resistant ulcers. Another trend is the growing preference for proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) over histamine receptor antagonists (H2 blockers) due to their superior acid-suppressing capabilities and faster onset of action. Additionally, there is a rising focus on the development of novel drug formulations with improved safety profiles and extended-release mechanisms to enhance patient adherence and minimize side effects. Moreover, advancements in diagnostic techniques, such as endoscopy and urea breath tests, are facilitating early detection and targeted treatment of peptic ulcers, driving demand for ulcer medications. Overall, these trends underscore the dynamic nature of the peptic ulcer drugs market as stakeholders strive to address evolving patient needs and optimize treatment outcomes.
Market Drivers:
Increasing prevalence of peptic ulcer disease:
The rising incidence of risk factors such as H. pylori infection, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) use, smoking, and stress contribute to the growing prevalence of peptic ulcers globally. As a result, there is a higher demand for effective pharmacological interventions to manage and treat peptic ulcers, driving the growth of the market for ulcer medications.
Technological advancements in drug delivery and formulation:
Ongoing research and development efforts have led to innovations in drug delivery systems and formulations for peptic ulcer drugs. Novel drug delivery technologies, such as controlled-release formulations and mucosal protective agents, offer improved efficacy, enhanced patient compliance, and reduced adverse effects compared to conventional formulations. These advancements drive market growth by expanding treatment options and improving patient outcomes in peptic ulcer management.
Market Restraints:
Despite advancements in treatment options, challenges such as the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains of H. pylori and the risk of adverse effects associated with long-term use of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) pose significant obstacles. Additionally, the availability of generic versions of some medications and the presence of alternative treatment modalities, such as dietary and lifestyle modifications, may limit the growth potential of the market. Moreover, stringent regulatory requirements for drug approval and the high cost of clinical trials for new drug development further hinder market expansion. Economic factors such as healthcare budget constraints and reimbursement limitations also impact market growth, particularly in developing regions where access to healthcare resources may be limited. Overall, these factors contribute to the challenges faced by stakeholders in the peptic ulcer drugs market.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the peptic ulcer drugs market. On one hand, the increased stress levels and changes in dietary habits during the pandemic may have led to a rise in the incidence of peptic ulcers, thereby driving the demand for ulcer medications. Additionally, individuals infected with COVID-19 may experience gastrointestinal symptoms, including ulcers, which could further contribute to market growth. However, on the other hand, disruptions in healthcare services, including delays in elective procedures and reduced patient visits to healthcare facilities, may have affected the diagnosis and treatment of peptic ulcers. Furthermore, supply chain disruptions and manufacturing challenges during the pandemic may have led to fluctuations in drug availability and pricing, impacting market dynamics. Overall, while the pandemic may have led to short-term fluctuations, the long-term impact of COVID-19 on the peptic ulcer drugs market remains to be fully understood as the situation continues to evolve.
Segmental Analysis:
Blood Test Segment is Expected to Witness Significant Growth Over the Forecast Period
Blood tests play a crucial role in the diagnosis and management of peptic ulcers. These tests help healthcare providers assess the severity of the ulcer, determine the underlying cause, and monitor the effectiveness of treatment. One of the most common blood tests used in peptic ulcer diagnosis is the Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) antibody test, which detects antibodies produced by the body in response to H. pylori infection, a common cause of peptic ulcers. Additionally, blood tests can help identify other potential causes of ulcers, such as the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or the presence of other infections. In terms of treatment, blood tests are not directly involved in the administration of peptic ulcer drugs. However, they are essential for monitoring the effects of these drugs on the body. For example, blood tests can help assess liver function and kidney function, which may be affected by certain ulcer medications. Additionally, blood tests can help monitor for any potential side effects of these drugs, such as changes in blood cell counts or electrolyte levels. Overall, blood tests are an integral part of the diagnostic and treatment process for peptic ulcers, helping healthcare providers make informed decisions about patient care.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPI) Segment is Expected to Witness Significant Growth Over the Forecast Period
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of drugs commonly used in the treatment of peptic ulcers. These medications work by reducing the production of stomach acid, which helps to alleviate symptoms and promote healing of the ulcers. PPIs are often prescribed for both duodenal ulcers (located in the upper part of the small intestine) and gastric ulcers (located in the stomach). One of the key benefits of PPIs in the treatment of peptic ulcers is their ability to provide long-lasting relief from symptoms. By reducing stomach acid production, PPIs help to reduce pain, discomfort, and inflammation associated with ulcers. Additionally, PPIs can help prevent complications such as bleeding or perforation of the ulcer. Commonly prescribed PPIs include omeprazole, lansoprazole, and esomeprazole. These medications are typically taken once daily, either before a meal or on an empty stomach, and are usually well-tolerated with few side effects. While PPIs are effective in treating peptic ulcers, they are not without risks. Long-term use of PPIs has been associated with an increased risk of certain side effects, such as bone fractures, vitamin B12 deficiency, and an increased risk of infections. Therefore, it is important for healthcare providers to carefully weigh the risks and benefits of PPI therapy for each individual patient. Thus, PPIs are a valuable class of medications for the treatment of peptic ulcers, providing effective relief from symptoms and promoting healing. However, their long-term use should be carefully monitored to minimize the risk of potential side effects.
Parenteral Segment is Expected to Witness Significant Growth Over the Forecast Period
The parenteral route of administration refers to the delivery of medications directly into the body through intravenous (IV), intramuscular (IM), or subcutaneous (SC) injection. While the oral route is the most common route for administering peptic ulcer drugs, the parenteral route may be used in certain situations, such as when a patient is unable to take medications orally due to severe symptoms or when rapid onset of action is needed. Intravenous administration of peptic ulcer drugs allows for the medication to be delivered directly into the bloodstream, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract and providing immediate systemic effects. This route is often used in hospitalized patients with severe or complicated ulcers, as it ensures that the medication is absorbed quickly and effectively. Intramuscular and subcutaneous injections of peptic ulcer drugs may be used when IV access is not available or when repeated doses are needed over a period of time. These routes of administration allow for the slow, gradual absorption of the medication into the bloodstream, providing sustained therapeutic effects. Thus, the parenteral route of administration is a valuable option for the delivery of peptic ulcer drugs in certain clinical scenarios, providing rapid and effective relief for patients with severe or complicated ulcers. However, the use of this route should be carefully considered based on the individual patient's condition and the specific characteristics of the medication being administered.
Hospitals Segment is Expected to Witness Significant Growth Over the Forecast Period
Hospitals play a critical role in the treatment of peptic ulcers, often serving as the primary setting for managing severe or complicated cases. Peptic ulcer drugs are an essential component of the treatment regimen for patients with ulcers admitted to hospitals. These medications are used to reduce stomach acid production, alleviate symptoms, and promote healing of the ulcers. In the hospital setting, peptic ulcer drugs are typically administered orally, intravenously, or through a nasogastric tube, depending on the patient's condition and the severity of the ulcer. Oral medications such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), histamine H2-receptor antagonists, and antacids are commonly used to reduce stomach acid levels and provide symptomatic relief. Intravenous administration of these medications may be necessary for patients who are unable to take oral medications or require more immediate relief. In addition to medication therapy, hospitals may also provide supportive care for patients with peptic ulcers, including dietary modifications, stress management techniques, and monitoring for complications such as bleeding or perforation. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair the ulcer or remove a portion of the stomach. Thus, hospitals play a crucial role in the management of peptic ulcers, providing comprehensive care that includes the use of peptic ulcer drugs to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. Through a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare providers from various specialties, hospitals can effectively treat peptic ulcers and improve patient outcomes.
North America Region is Expected to Witness Significant Growth Over the Forecast Period
North America is a significant market for peptic ulcer drugs, driven by several factors such as the high prevalence of peptic ulcers, the availability of advanced healthcare infrastructure, and the presence of key market players. Peptic ulcers, which include gastric ulcers and duodenal ulcers, are common in North America, affecting millions of people each year. In the United States and Canada, healthcare providers have access to a wide range of peptic ulcer drugs, including proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), histamine H2-receptor antagonists, and antibiotics to treat Helicobacter pylori infection, a common cause of peptic ulcers. These medications are often prescribed in combination to provide effective symptom relief and promote ulcer healing. North America's advanced healthcare infrastructure and high-quality medical care contribute to the effective management of peptic ulcers. Patients in the region have access to skilled healthcare professionals who can diagnose and treat ulcers promptly, reducing the risk of complications. Moreover, the presence of key pharmaceutical companies in North America contributes to the development and availability of innovative peptic ulcer drugs. These companies invest in research and development to improve existing treatments and develop new therapies, further driving market growth. Thus, North America is a significant market for peptic ulcer drugs, characterized by high prevalence rates, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and a strong pharmaceutical industry presence. These factors contribute to the effective management of peptic ulcers and drive growth in the region's peptic ulcer drugs market.
Get Complete Analysis Of The Report - Download Free Sample PDF
The analyzed market exhibits a high degree of fragmentation, primarily attributable to the presence of numerous players operating on both a global and regional scale. The competitive landscape is characterized by a diverse array of companies, each contributing to the overall market dynamics. This fragmentation arises from the existence of specialized solution providers, established industry players, and emerging entrants, all vying for market share. The diversity in market participants is underscored by the adoption of various strategies aimed at expanding the company presence. On a global scale, companies within the studied market are strategically positioning themselves through aggressive expansion initiatives. This often involves entering new geographical regions, targeting untapped markets, and establishing a robust global footprint. The pursuit of global expansion is driven by the recognition of diverse market opportunities and the desire to capitalize on emerging trends and demands across different regions. Simultaneously, at the regional level, companies are tailoring their approaches to align with local market dynamics. Regional players are leveraging their understanding of specific market nuances, regulatory environments, and consumer preferences to gain a competitive edge. This regional focus allows companies to cater to the unique needs of local clientele, fostering stronger market penetration. To navigate the complexities of the fragmented market, companies are implementing a range of strategies. These strategies include investments in research and development to stay at the forefront of technological advancements, mergers and acquisitions to consolidate market share, strategic partnerships for synergies, and innovation to differentiate products and services. The adoption of such multifaceted strategies reflects the competitive nature of the market, with participants continually seeking avenues for growth and sustainability. In essence, the high fragmentation in the studied market not only signifies the diversity of players but also underscores the dynamism and competitiveness that drive ongoing strategic maneuvers. As companies explore various avenues for expansion, the market continues to evolve, presenting both challenges and opportunities for industry stakeholders.
Some of the major players operating in the gastric ulcers market are:
Recent Developments:
1) In April 2023, Akums Drugs and Pharmaceuticals unveiled a groundbreaking addition to its product line: a unique Combikit containing a combination of Amoxicillin, Clarithromycin, and Esomeprazole. This Combikit marks a pioneering entry into the Indian market for Akums, as it is the first of its kind to be introduced by the company in the country. The introduction of this innovative Combikit is poised to drive significant growth in the gastric ulcers market. Gastric ulcers are a common gastrointestinal disorder that can cause considerable discomfort and health complications. The combination of Amoxicillin, Clarithromycin, and Esomeprazole in the Combikit offers a comprehensive and effective treatment option for gastric ulcers.
2) In 2021, Pharma major Dr. Reddy's Laboratories launched generic Chlordiazepoxide Hydrochloride and Clidinium Bromide capsules in the US market. These capsules were used for the treatment of stomach ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome, and inflammation of the colon. The company had launched Chlordiazepoxide Hydrochloride and Clidinium Bromide capsules USP, 5 mg/2.5 mg in the US market, as stated in a regulatory announcement by Dr. Reddy's Laboratories.
Q1. What was the Peptic Ulcer Drugs Market size in 2023?
As per Data Library Research the peptic ulcer drugs market size was valued at USD 6.2 in 2023.
Q2. At what CAGR is the Peptic Ulcer Drugs market projected to grow within the forecast period?
Peptic Ulcer Drugs Market is projected to reach a CAGR of 2.4% in forecast period.
Q3. What are the Growth Drivers of the Peptic Ulcer Drugs Market?
Increasing prevalence of peptic ulcer disease and Technological advancements in drug delivery and formulation are the Growth Drivers of the Peptic Ulcer Drugs Market.
Q4. Which region has the largest share of the Peptic Ulcer Drugs market? What are the largest region's market size and growth rate?
North America has the largest share of the market. For detailed insights on the largest region's market size and growth rate request a sample here.
Data Library Research are conducted by industry experts who offer insight on industry structure, market segmentations technology assessment and competitive landscape (CL), and penetration, as well as on emerging trends. Their analysis is based on primary interviews (~ 80%) and secondary research (~ 20%) as well as years of professional expertise in their respective industries. Adding to this, by analysing historical trends and current market positions, our analysts predict where the market will be headed for the next five years. Furthermore, the varying trends of segment & categories geographically presented are also studied and the estimated based on the primary & secondary research.
In this particular report from the supply side Data Library Research has conducted primary surveys (interviews) with the key level executives (VP, CEO’s, Marketing Director, Business Development Manager and SOFT) of the companies that active & prominent as well as the midsized organization
FIGURE 1: DLR RESEARH PROCESS
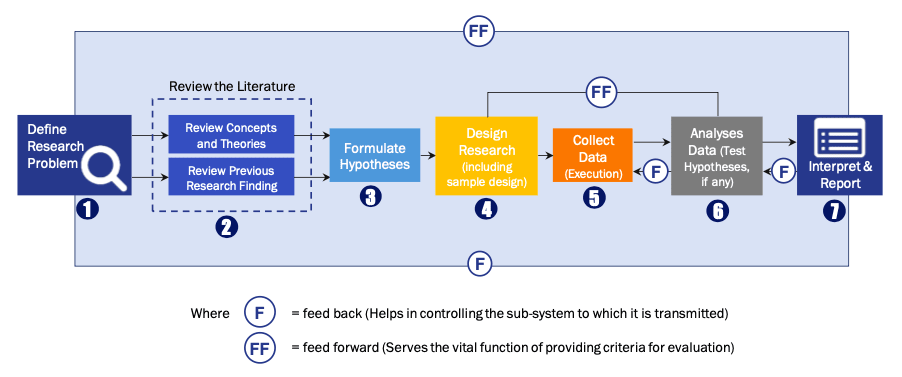
Extensive primary research was conducted to gain a deeper insight of the market and industry performance. The analysis is based on both primary and secondary research as well as years of professional expertise in the respective industries.
In addition to analysing current and historical trends, our analysts predict where the market is headed over the next five years.
It varies by segment for these categories geographically presented in the list of market tables. Speaking about this particular report we have conducted primary surveys (interviews) with the key level executives (VP, CEO’s, Marketing Director, Business Development Manager and many more) of the major players active in the market.
Secondary ResearchSecondary research was mainly used to collect and identify information useful for the extensive, technical, market-oriented, and Friend’s study of the Global Extra Neutral Alcohol. It was also used to obtain key information about major players, market classification and segmentation according to the industry trends, geographical markets, and developments related to the market and technology perspectives. For this study, analysts have gathered information from various credible sources, such as annual reports, sec filings, journals, white papers, SOFT presentations, and company web sites.
Market Size EstimationBoth, top-down and bottom-up approaches were used to estimate and validate the size of the Global market and to estimate the size of various other dependent submarkets in the overall Extra Neutral Alcohol. The key players in the market were identified through secondary research and their market contributions in the respective geographies were determined through primary and secondary research.
Forecast Model