Get Complete Analysis Of The Report - Download Updated Free Sample PDF
The Global Systemic Infection Treatment Drugs Market is experiencing strong growth driven primarily by the rising global burden of bacterial, viral, fungal, and parasitic infections, fueled by increasing urbanization, climate change–related disease spread, and higher antimicrobial resistance (AMR) rates. The expanding need for broad-spectrum and targeted therapies, along with growing hospital admissions and ICU procedures, is accelerating demand for effective systemic anti-infective drugs.
The systemic infection treatment drugs market is increasingly driven by rising levels of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), prompting urgent demand for novel antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals — and pushing pharmaceutical firms to accelerate R&D into narrow-spectrum and pathogen-specific therapies that can more effectively tackle resistant infections. At the same time, there is growing uptake of advanced therapeutics such as combination therapies, biologics, and immune-modulating agents aimed at treating complex or drug-resistant systemic infections; this expansion beyond traditional broad-spectrum antibiotics reflects a shift toward precision medicine and improved safety/efficacy profiles.
Segmentation: Global Systemic Infection Treatment Drugs Market is segmented By Drug Class (Antibiotics, Antivirals, Antifungals, Antiparasitic Drugs), Infection Type (Bacterial Systemic Infections, Viral Systemic Infections, Fungal Systemic Infections, Parasitic Systemic Infections), Route of Administration (Oral, Intravenous, Intramuscular, Subcutaneous), Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, Online Pharmacies), End User (Hospitals, Specialty & Multispecialty Clinics, Home Healthcare Settings), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa, and South America). The report provides the value (in USD million) for the above segments.
For Detailed Market Segmentation - Get a Free Sample PDF
Market Drivers:
The increasing global burden of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a major force driving the demand for advanced systemic infection treatment drugs. Overuse and misuse of antibiotics, especially in developing regions, have accelerated the emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria, viruses, and fungi. For instance, in November 2023, Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) not only increases mortality and morbidity but also imposes heavy economic burdens. The World Bank estimates AMR could add USD 1 trillion in healthcare costs by 2050 and cause annual GDP losses of USD 1–3.4 trillion by 2030, intensifying demand for effective systemic infection treatment drugs.
Conditions such as MRSA, VRE, CRE, drug-resistant TB, and resistant bloodstream infections are becoming more common, prompting healthcare systems to adopt more potent, broad-spectrum, and targeted systemic therapies. Governments and global health agencies are investing heavily in antimicrobial stewardship programs, novel drug development, and rapid diagnostics—further contributing to market growth as newer, more effective systemic treatment options are prioritized.
The rising global incidence of systemic infections caused by bacterial sepsis, viral outbreaks, invasive fungal infections, and parasitic diseases continues to propel drug demand. Hospital-acquired infections (HAIs)—such as bloodstream infections, surgical-site infections, ventilator-associated pneumonia, and catheter-associated UTIs—are increasing due to overcrowded hospitals and higher numbers of immunocompromised patients. For instance, in 2022, CDC reported that, in 2015, approximately 3% of U.S. hospital patients—about 687,000—acquired healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), resulting in 72,000 deaths. The rising incidence of severe infections and HAIs is driving demand for effective systemic infection treatment drugs globally.
Additionally, aging populations and chronic disease prevalence significantly elevate susceptibility to severe systemic infections. These trends are driving healthcare providers to adopt rapid therapeutic interventions and advanced systemic treatment regimens, which strengthens growth across antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, and immunomodulator segments.
Market Restraints:
A major restraint in the global systemic infection treatment drugs market is the rising prevalence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Overuse and misuse of antibiotics and antiviral medications reduce drug effectiveness, leading to treatment failures and prolonged infections. This increases healthcare costs, limits therapeutic options, and discourages investment in certain drug segments. Additionally, stringent regulatory approvals and high research and development costs for new systemic infection drugs pose significant barriers for pharmaceutical companies. These challenges collectively slow market growth, restrict the introduction of innovative therapies, and create uncertainties for stakeholders aiming to address systemic infections effectively on a global scale.
The global systemic infection treatment drugs market has significant socioeconomic impact by improving public health outcomes and reducing mortality from bacterial, viral, and fungal infections worldwide. Widespread availability of effective systemic treatments decreases the burden on healthcare systems, shortens hospital stays, and lowers associated treatment costs. Improved infection management enhances workforce productivity and reduces economic losses from illness-related absenteeism. Access to advanced systemic infection drugs also strengthens health equity by addressing infectious disease risks in developing and underserved regions. Furthermore, the market drives pharmaceutical research and innovation, creating jobs in drug development, manufacturing, and distribution, contributing to broader economic growth.
Segmental Analysis:
Antibiotics remain the largest and most critical segment due to the persistent prevalence of bacterial systemic infections, including sepsis, bloodstream infections, and hospital-acquired infections. Broad-spectrum and targeted antibiotics are widely used in hospitals and clinics to manage severe infections and prevent complications. The rising threat of multidrug-resistant bacterial strains has further fueled demand for newer, potent antibiotics, driving research, development, and adoption of advanced therapies globally.
Bacterial systemic infections account for a significant portion of market growth, as they are among the most common and life-threatening infections worldwide. Conditions such as sepsis, pneumonia-related bloodstream infections, and resistant bacterial infections require immediate systemic intervention. The increasing incidence of hospital-acquired bacterial infections and antimicrobial resistance is further elevating demand for effective systemic therapies to improve patient outcomes.
Intravenous (IV) administration is the preferred route for severe systemic infections because it ensures rapid drug delivery, higher bioavailability, and immediate therapeutic effects. IV drugs are commonly used in hospital settings for critically ill patients and those with complications, including bloodstream infections, sepsis, and invasive fungal infections. The demand for IV systemic infection treatments is rising due to increasing hospitalizations and acute infection management requirements.
Hospital pharmacies are the leading distribution channel for systemic infection treatment drugs, as hospitals are the primary point of care for severe infections. Hospital pharmacies provide access to high-value, prescription-only systemic therapies, including IV antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals, ensuring timely administration under medical supervision. This channel also facilitates the use of advanced therapies in intensive care units and critical care settings.
Hospitals represent the largest end-user segment due to their role in managing acute and severe systemic infections. With increasing hospitalization rates, aging populations, and the prevalence of immunocompromised patients, hospitals rely heavily on systemic infection drugs for effective treatment. The availability of advanced diagnostic tools and intensive care facilities further strengthens hospital demand for systemic therapies.
North America holds a dominant position in the market due to high healthcare spending, advanced medical infrastructure, and strong adoption of next-generation systemic infection therapies. The region faces rising incidences of hospital-acquired infections and multidrug-resistant pathogens, which drive demand for potent antibiotics, antivirals, and antifungals. Additionally, government initiatives supporting antimicrobial stewardship, rapid diagnostics, and research investments contribute to regional market growth.
The U.S. market specifically drives North America’s dominance, supported by well-established pharmaceutical companies, extensive research and development capabilities, and widespread access to advanced healthcare facilities. Rising awareness among healthcare providers and patients about multidrug-resistant infections has accelerated the adoption of next-generation systemic infection drugs.
Continuous investments in clinical trials, innovative drug formulations, and rapid diagnostic technologies further strengthen the market. For instance, in August 2025, Celltrion, Inc. announced FDA approval for an expanded indication of AVTOZMA® (tocilizumab-anoh) IV to treat cytokine release syndrome (CRS) in adults and children aged 2 and above. This broadens therapeutic options, aligns AVTOZMA with ACTEMRA® IV indications, and strengthens the U.S. systemic infection treatment drugs market by enhancing access to critical immunomodulatory therapies. Moreover, federal programs promoting antimicrobial stewardship and infection control in hospitals enhance the demand for effective therapies, positioning the U.S. as a critical hub for the development, commercialization, and consumption of systemic infection treatment drugs within North America.
To Learn More About This Report - Request a Free Sample Copy
The competitive landscape of the Global Systemic Infection Treatment Drugs Market is highly dynamic, characterized by intense competition among multinational pharmaceutical companies, specialty biotech firms, and regional generics manufacturers. Key players focus on developing innovative antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, and antiparasitic drugs to address rising antimicrobial resistance and severe systemic infections. Companies compete through strategic partnerships, mergers and acquisitions, research and development investments, and the introduction of combination therapies and biologics. Rapid advancements in diagnostics, personalized medicine, and regulatory approvals also shape competitive strategies, enabling companies to expand their product portfolios and strengthen their global market presence.
Key Players:
Recent Development
Q1. What are the main growth-driving factors for this market?
The market is primarily driven by the rising global prevalence of infectious diseases and the increasing geriatric population, which is more vulnerable to infections. Continuous emergence of drug-resistant pathogens requires constant research and development of new, innovative anti-infective drugs.
Q2. What are the main restraining factors for this market?
The biggest obstacle is the rapid development of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), which quickly renders current drugs ineffective and necessitates high R&D costs for replacements. Additionally, stringent regulatory approval processes and the high cost of developing and marketing new treatments limit market access.
Q3. Which segment is expected to witness high growth?
The antiviral drugs segment is anticipated to witness significant growth, largely driven by the ongoing threat from novel viral outbreaks and the need for improved treatments for widespread conditions like HIV and Hepatitis. The hospital pharmacies distribution channel is also expected to maintain dominance.
Q4. Who are the top major players for this market?
The market is dominated by established global pharmaceutical giants. Key companies include Merck & Co., Inc., Pfizer, Inc., GlaxoSmithKline Plc. (GSK), Roche, and Novartis AG. These firms lead in developing and supplying a broad range of antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal therapies.
Q5. Which country is the largest player?
The United States dominates the systemic infection treatment drugs market, leading in overall revenue. This is due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high healthcare spending, established pharmaceutical R&D ecosystem, and favorable reimbursement policies for costly, novel anti-infective drugs.
Data Library Research are conducted by industry experts who offer insight on industry structure, market segmentations technology assessment and competitive landscape (CL), and penetration, as well as on emerging trends. Their analysis is based on primary interviews (~ 80%) and secondary research (~ 20%) as well as years of professional expertise in their respective industries. Adding to this, by analysing historical trends and current market positions, our analysts predict where the market will be headed for the next five years. Furthermore, the varying trends of segment & categories geographically presented are also studied and the estimated based on the primary & secondary research.
In this particular report from the supply side Data Library Research has conducted primary surveys (interviews) with the key level executives (VP, CEO’s, Marketing Director, Business Development Manager and SOFT) of the companies that active & prominent as well as the midsized organization
FIGURE 1: DLR RESEARH PROCESS
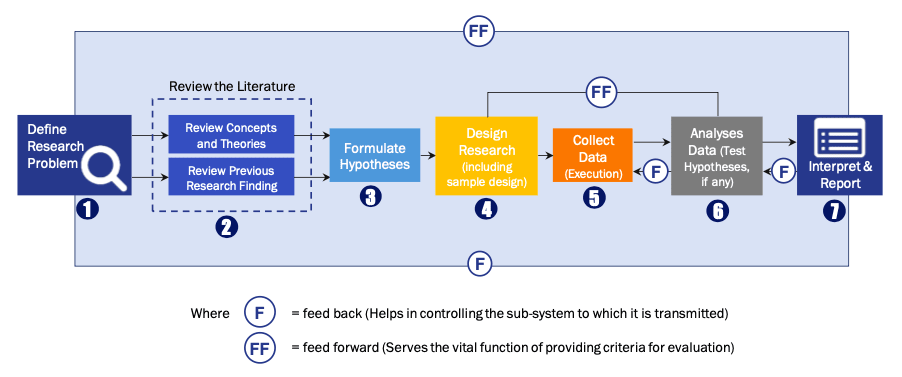
Extensive primary research was conducted to gain a deeper insight of the market and industry performance. The analysis is based on both primary and secondary research as well as years of professional expertise in the respective industries.
In addition to analysing current and historical trends, our analysts predict where the market is headed over the next five years.
It varies by segment for these categories geographically presented in the list of market tables. Speaking about this particular report we have conducted primary surveys (interviews) with the key level executives (VP, CEO’s, Marketing Director, Business Development Manager and many more) of the major players active in the market.
Secondary ResearchSecondary research was mainly used to collect and identify information useful for the extensive, technical, market-oriented, and Friend’s study of the Global Extra Neutral Alcohol. It was also used to obtain key information about major players, market classification and segmentation according to the industry trends, geographical markets, and developments related to the market and technology perspectives. For this study, analysts have gathered information from various credible sources, such as annual reports, sec filings, journals, white papers, SOFT presentations, and company web sites.
Market Size EstimationBoth, top-down and bottom-up approaches were used to estimate and validate the size of the Global market and to estimate the size of various other dependent submarkets in the overall Extra Neutral Alcohol. The key players in the market were identified through secondary research and their market contributions in the respective geographies were determined through primary and secondary research.
Forecast Model